30 Most Cultivated Vegetables In The World

Feeding billions every day, these vegetables are the true global staples. From humble roots to leafy greens, vegetables are a core part of human diets worldwide. Whether they’re fried, steamed, fermented, or eaten raw, these crops are grown in massive quantities across continents. Based on global cultivation and production data, here are the 30 most widely grown vegetables in the world.
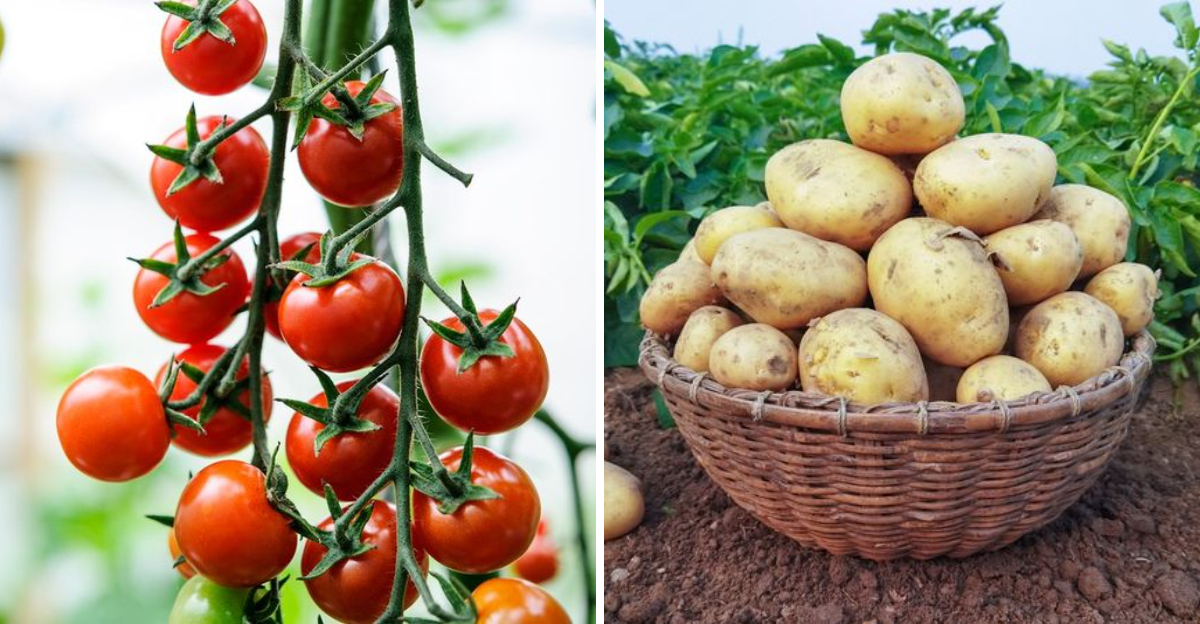
1. Tomatoes
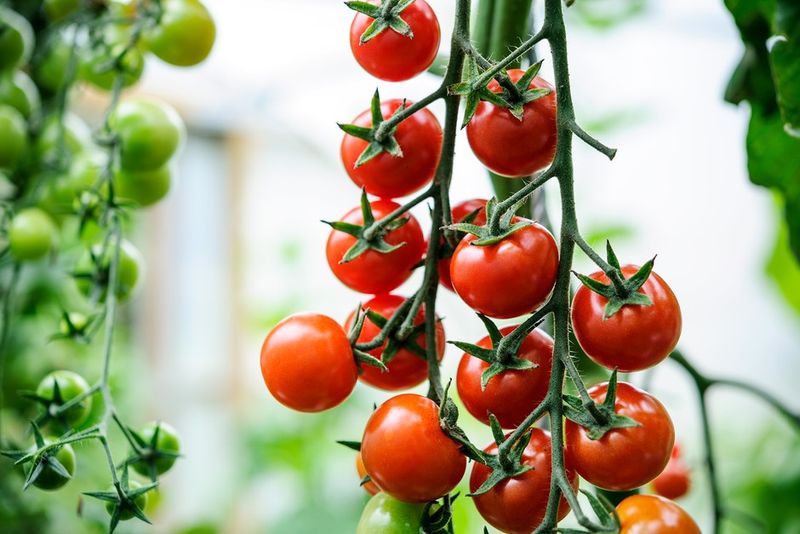

Often considered both a fruit and a vegetable, tomatoes are a culinary chameleon. These vibrant red spheres are the centerpiece of dishes worldwide. Their juicy flesh and tangy taste add a burst of flavor to salads, sauces, and soups.
In Mediterranean regions, tomatoes bask in the sun, enhancing their sweet, rich notes. Meanwhile, in colder climates, greenhouses allow them to thrive year-round. Fun fact: the debate over tomatoes’ classification has sparked many a dinner table discussion.
When it comes to global cuisine, this versatile ingredient is virtually unrivaled in its ubiquity.
2. Potatoes
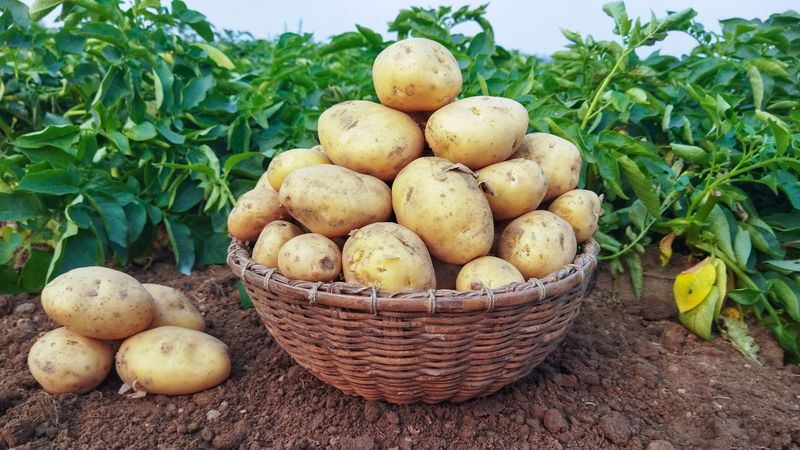

A true staple, potatoes boast an impressive versatility that has endeared them to kitchens across the globe. Whether mashed, fried, or baked, their comforting texture and hearty flavor are a culinary cornerstone.
European, Asian, and American diets all celebrate the humble potato, using it as a base for countless traditional dishes. In Ireland, they are famously associated with sustenance through hard times.
From crispy fries to creamy soups, the potato’s adaptability is its strength. Interestingly, they were first cultivated in the Andes Mountains over 7,000 years ago.
3. Onions
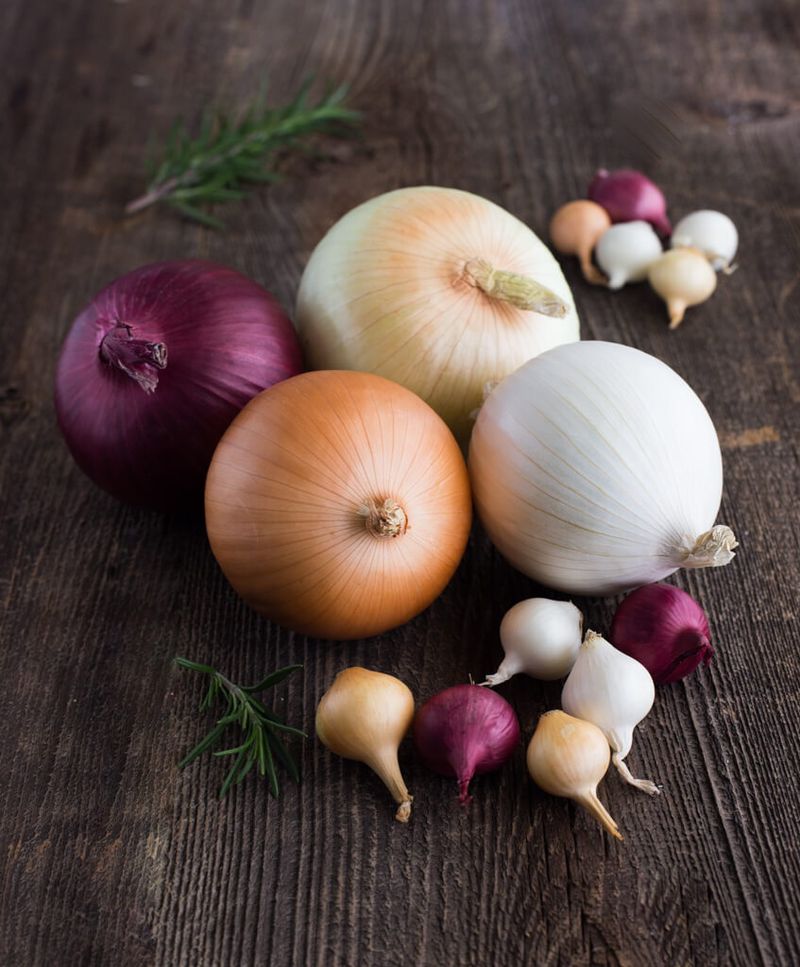

Onions, with their robust aroma and flavor, are the unsung heroes of the kitchen. Used in almost every cuisine, they build the flavor foundation for dishes around the world.
From curries in India to soups in France, onions are integral to culinary traditions. Their ability to transform a dish with their sweetness and depth is unmatched.
Despite their tear-inducing reputation, onions have been revered for centuries for their health benefits and flavor-enhancing qualities. Did you know? Ancient Egyptians considered onions a symbol of eternal life.
4. Cabbage
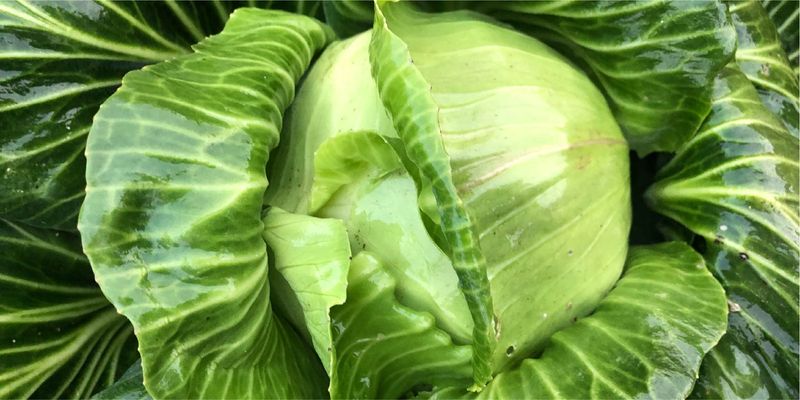

Cabbage, with its crisp texture and slightly peppery taste, is a vegetable of many faces. Used in a variety of culinary applications, from crunchy slaws to hearty stews, it holds a significant place in global diets.
Asia and Europe particularly cherish cabbage, where it forms the basis of fermented foods like sauerkraut and kimchi. These dishes not only preserve the vegetable but also enhance its nutritional value.
An ancient crop, cabbage was a staple in Roman times, valued for its storage longevity and versatility. Today, it continues to adapt to modern culinary trends.
5. Garlic
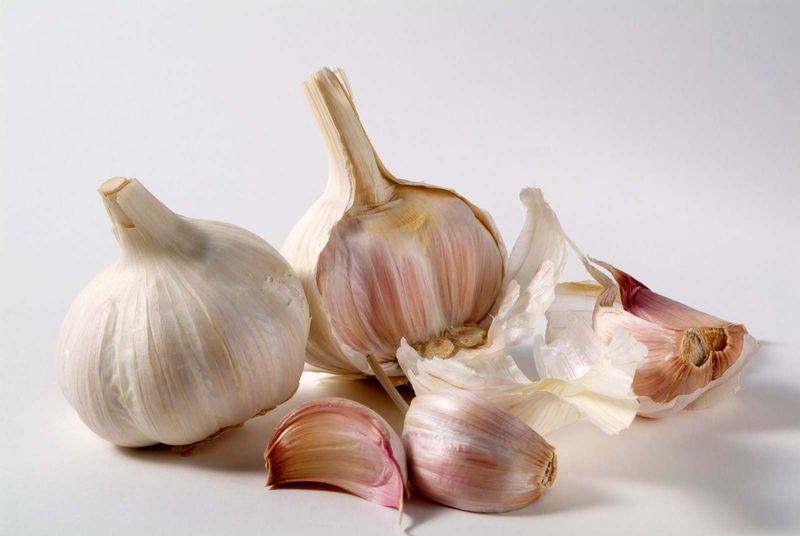

Garlic, the small yet mighty bulb, is a powerhouse of flavor. Its pungent aroma and savory taste make it an indispensable ingredient in countless dishes.
From Italian pasta to Asian stir-fries, garlic’s presence is felt globally. Its ability to enhance and complement other flavors is legendary. Historically, garlic has been prized not only for its culinary uses but also for its medicinal properties.
In ancient times, it was even used in rituals and as currency. Despite its size, garlic’s impact on the culinary world is monumental, making it a kitchen staple.
6. Carrots

With their bright orange hue and sweet, earthy flavor, carrots are a favorite in kitchens worldwide. This humble root vegetable is loved for its versatility and nutritional profile.
Carrots can be enjoyed raw, cooked, or juiced, making them a staple in salads, soups, and snacks. In many cultures, they symbolize health and vitality, often included in dishes for their vibrant color and natural sweetness.
Interestingly, carrots were originally purple and evolved into the orange variety we know today. A nutritious and colorful addition to any meal, carrots are truly timeless.
7. Lettuce
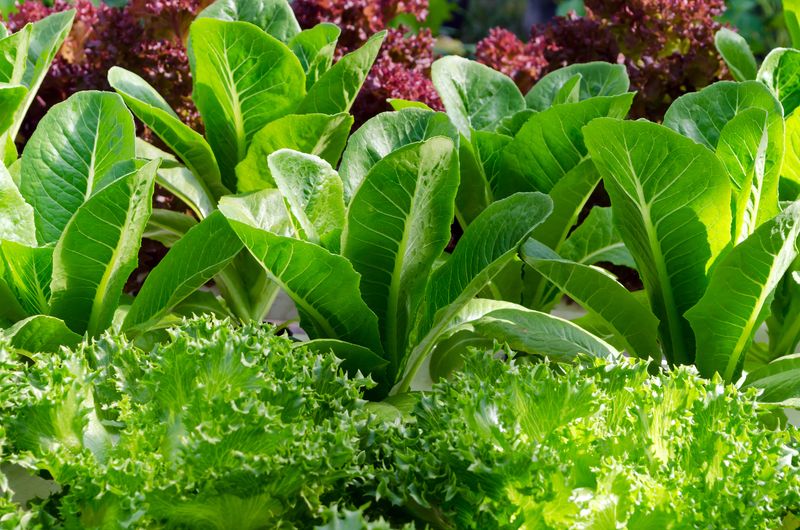

Synonymous with fresh salads, lettuce is the go-to leafy green for many. Its crisp texture and mild flavor make it a refreshing addition to a variety of dishes.
From gourmet burgers to simple side salads, lettuce is incredibly versatile. In the U.S. and Europe, it’s a staple in many diets, valued for its low calorie content and hydrating properties.
Throughout history, lettuce has been cultivated for its leaves and stems, with ancient Egyptians considering it a symbol of fertility. Today, it remains a symbol of freshness and health.
8. Cucumbers
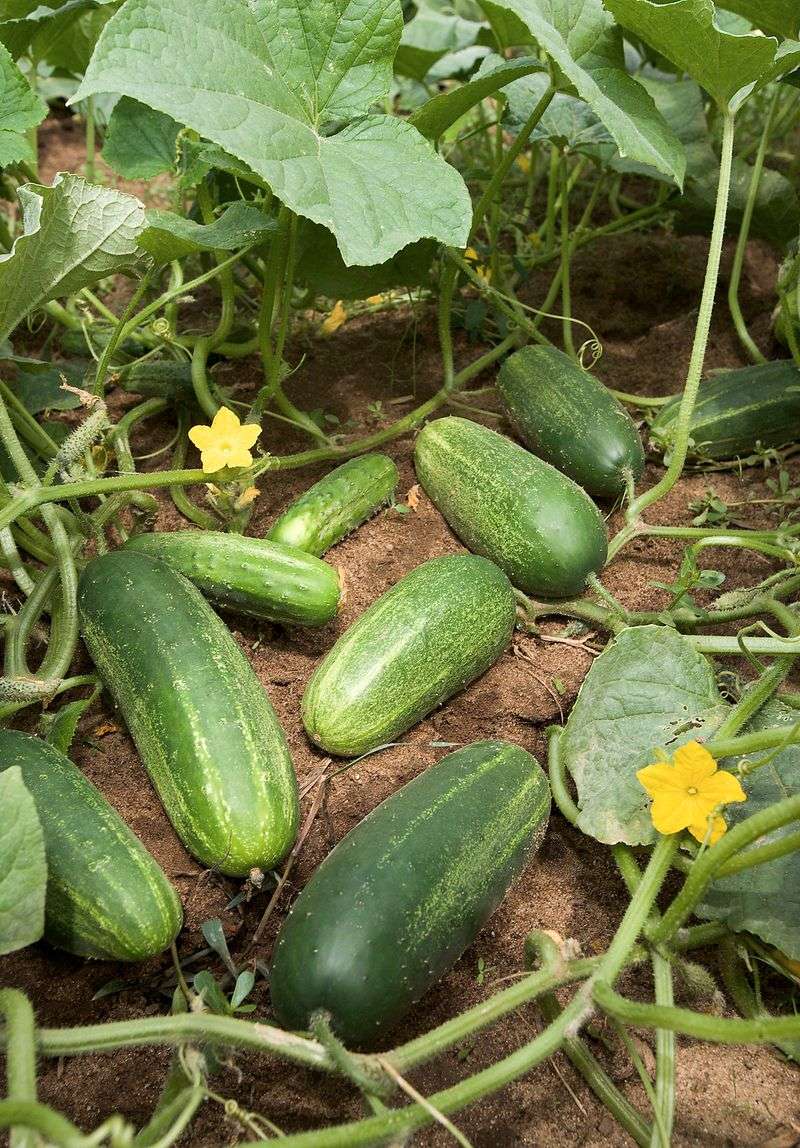

The cool, refreshing taste of cucumbers makes them a beloved vegetable around the globe. Often consumed raw, their crisp texture is a staple in salads and sandwiches.
In many cultures, cucumbers are also pickled, enhancing their flavor and extending their shelf life. They are grown in over 100 countries, adapting well to various climates.
Beyond their culinary uses, cucumbers are known for their hydrating properties and are often used in beauty treatments. Did you know? Cucumbers are mostly water, making them a great low-calorie snack for warm days.
9. Eggplant (Aubergine)
Eggplants, with their glossy purple skin and spongy flesh, are a staple in many cuisines. Their ability to absorb flavors makes them a versatile component in dishes like ratatouille and baba ganoush.
In Asia, the Middle East, and the Mediterranean, eggplant is celebrated in a variety of traditional recipes. Its unique texture and mild taste allow it to pair well with bold spices and flavors.
Originally from India, eggplant has been cultivated for centuries, evolving into the diverse varieties we see today. Its culinary adaptability continues to inspire chefs worldwide.
10. Peppers (Bell and Chili)
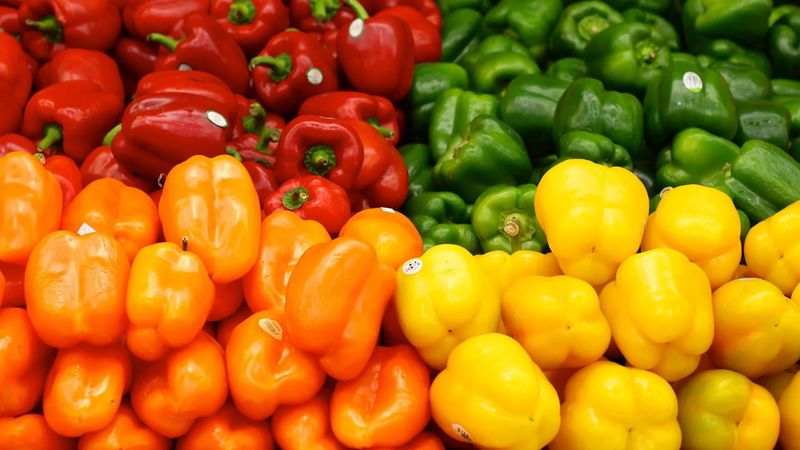

Peppers, in their myriad of colors and flavors, are a global favorite. From the sweet bell peppers to the fiery chilies, they add both color and heat to dishes.
Cultures around the world have embraced peppers, using them in salsas, stir-fries, and hot sauces. Their vibrant hues and distinct flavors make them a versatile ingredient in countless recipes.
Interestingly, peppers are native to the Americas and have been cultivated for thousands of years. Today, their popularity continues to grow, adding spice and excitement to meals everywhere.
11. Sweet Corn (Maize)
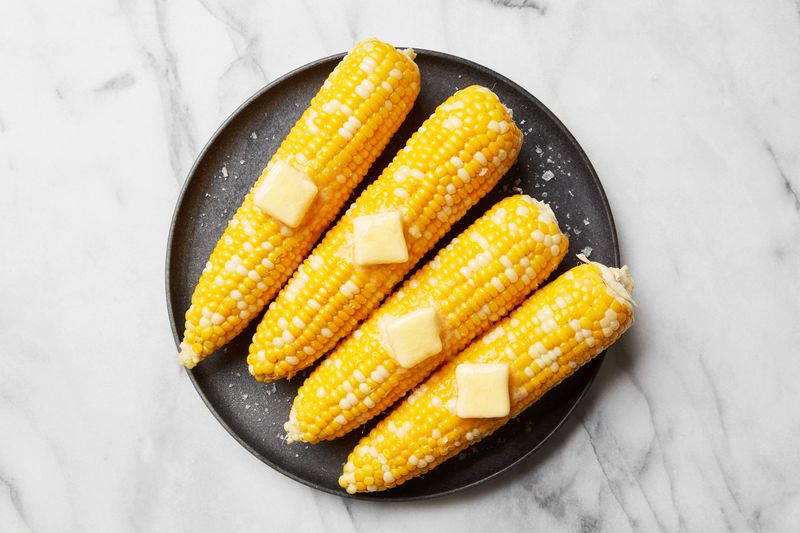

Sweet corn, with its juicy kernels, is a beloved vegetable across continents. While technically a grain, it is widely used as a vegetable in cooking.
From corn on the cob to creamed corn, this versatile ingredient is a summer favorite. In many cultures, it holds significant cultural and historical importance, particularly among Native American tribes.
Sweet corn’s natural sweetness and tender texture make it a popular choice for both savory and sweet dishes. Its ability to adapt to different culinary styles is a testament to its enduring appeal.
12. Spinach
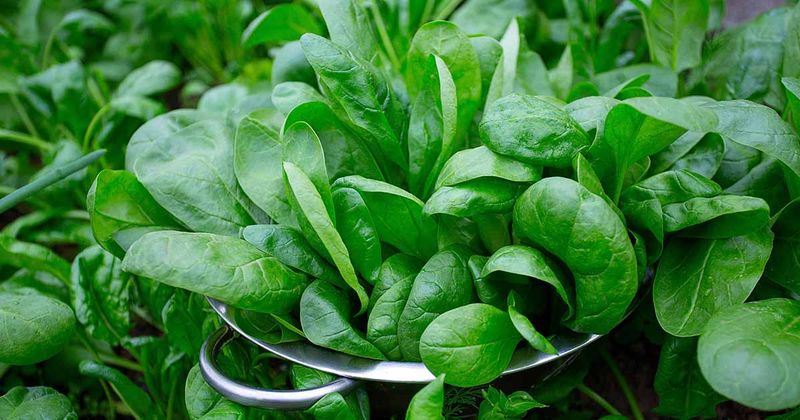

Spinach, the iron-rich leafy green, is a culinary powerhouse. Its tender leaves and mild flavor make it a versatile ingredient in dishes ranging from smoothies to curries.
In many cultures, spinach is celebrated for its nutritional benefits, often included in diets for its high vitamin and mineral content. It can be enjoyed raw in salads or cooked in a variety of savory dishes.
Did you know? Spinach was once a favorite of the Persian Empire before spreading across the globe. Today, it remains a symbol of health and vitality in culinary traditions worldwide.
13. Green Beans
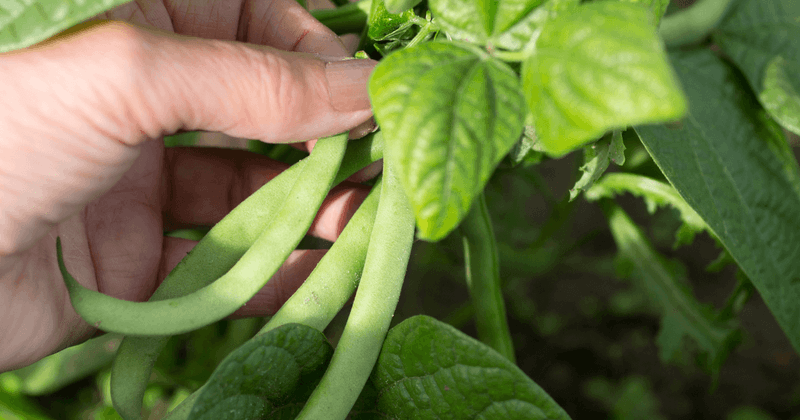

Green beans, with their crisp texture and vibrant color, are a popular vegetable choice for many. They are cultivated on nearly every continent, showcasing their adaptability and appeal.
Often served steamed or stir-fried, green beans add a refreshing crunch to meals. In many cuisines, they are a staple side dish, complementing a variety of main courses.
Historically, green beans have been grown for thousands of years, with origins traced back to Central and South America. Today, they continue to be a favorite for their simplicity and nutritional benefits.
14. Broccoli
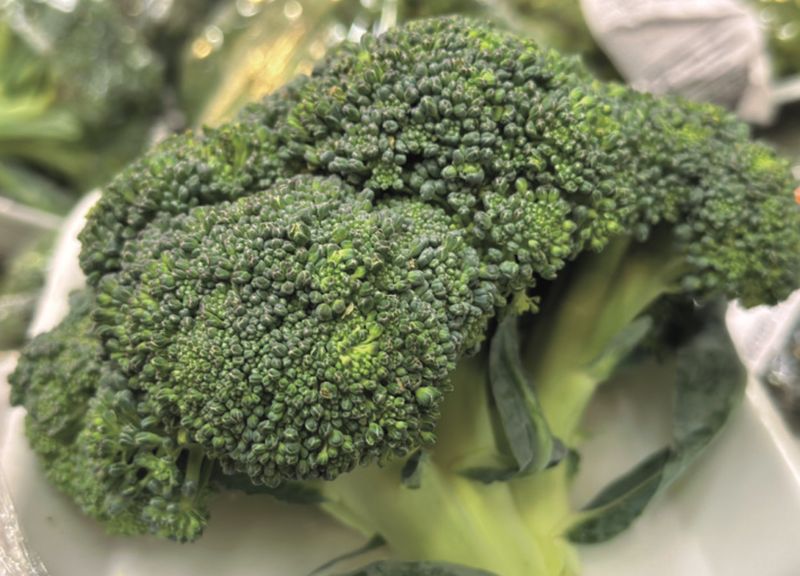

Broccoli, with its tree-like appearance, is a beloved vegetable rich in nutrients. Often dubbed a superfood, it is celebrated for its high vitamin content and health benefits.
In Europe, China, and the U.S., broccoli is a staple in many diets, enjoyed steamed, roasted, or raw. Its slightly bitter taste and hearty texture make it a versatile addition to a variety of dishes.
Did you know? Broccoli is a member of the brassica family, which also includes cabbage and kale. Its popularity continues to rise as health-conscious consumers seek nutritious options.
15. Cauliflower
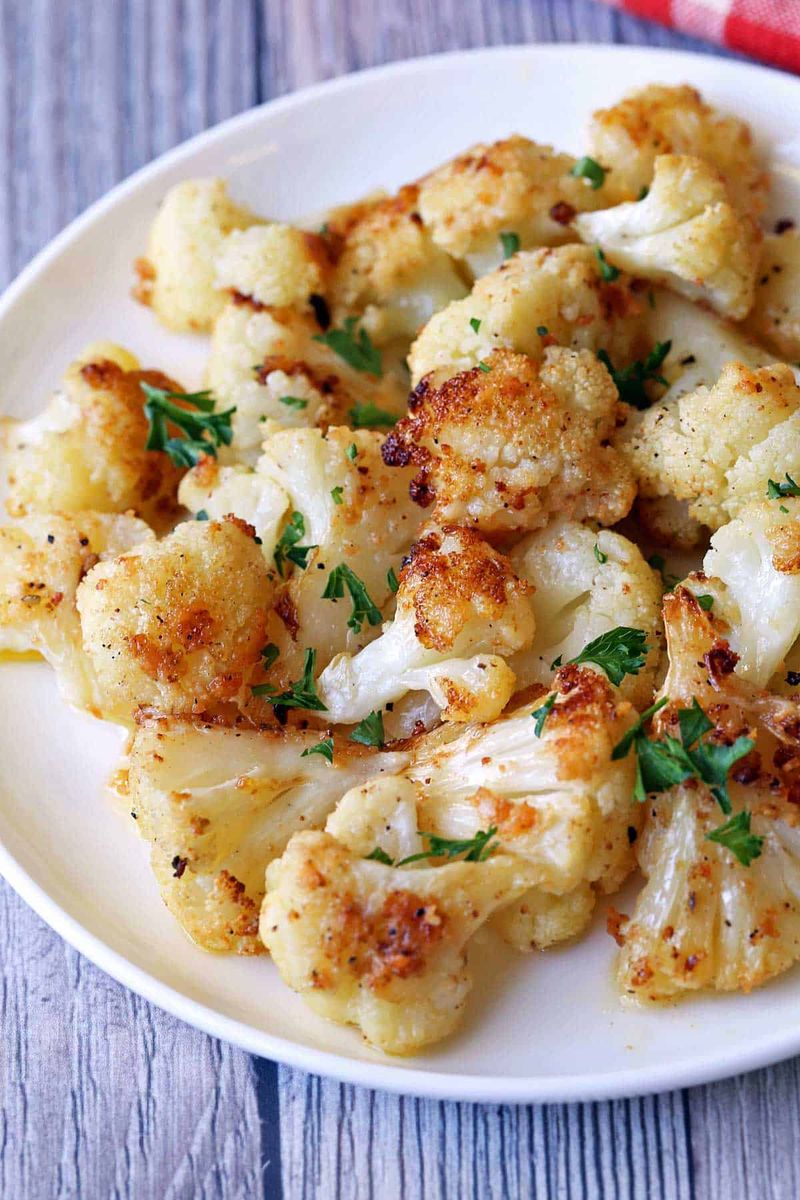

Cauliflower, with its creamy white florets, is a versatile vegetable that has recently gained popularity. As a low-carb alternative, it is often used in rice, pizza crusts, and more.
Closely related to broccoli, cauliflower shares a similar texture and flavor profile. Its mild taste allows it to blend seamlessly into a variety of dishes, from curries to roasted sides.
Interestingly, cauliflower has been cultivated for centuries, originally from the Mediterranean region. Today, it continues to adapt to modern culinary trends, offering a nutritious and adaptable option for many diets.
16. Zucchini (Courgette)
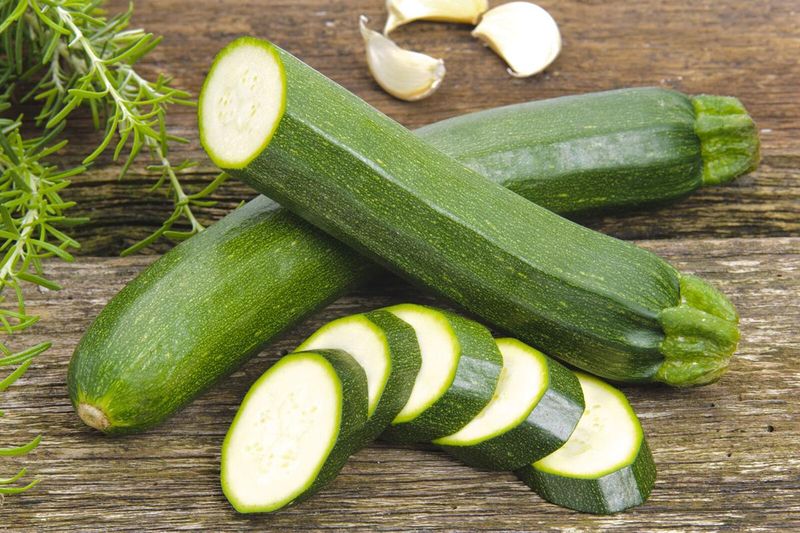

Zucchini, with its tender flesh and mild flavor, is a warm-weather squash beloved by many. Its versatility allows it to shine in both sweet and savory dishes, from breads to stir-fries.
In summer gardens, zucchini plants flourish, producing an abundance of fruits. Their delicate taste pairs well with a variety of ingredients, making them a staple in cuisines worldwide.
Originally from Central America, zucchini has traveled far, adapting to diverse culinary traditions. Its popularity continues to grow, especially as health-conscious eaters seek low-calorie, nutritious options.
17. Peas
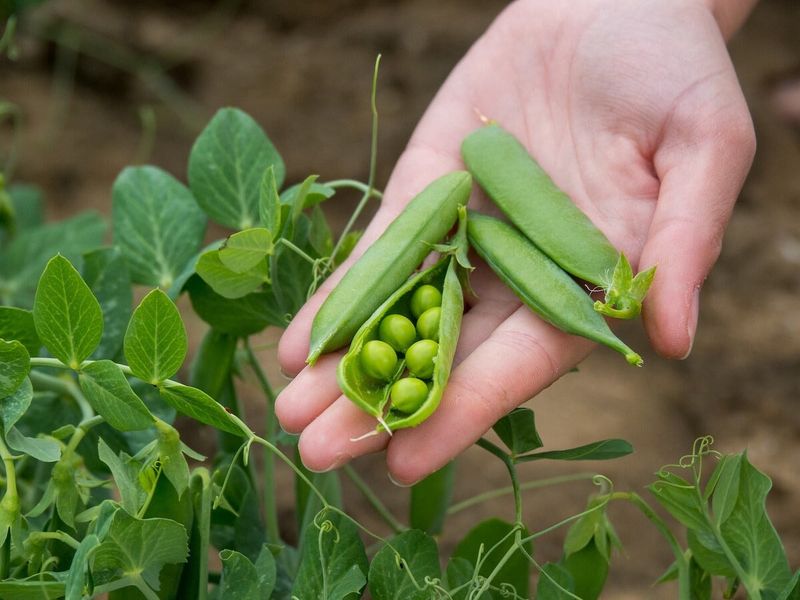

Peas, with their vibrant green hue and sweet flavor, are a favorite in many kitchens. These small, round vegetables are often frozen to ensure year-round availability.
In temperate zones, peas are easily grown, making them a staple in many diets. They add a pop of color and an element of sweetness to a variety of dishes, from soups to salads.
Historically, peas have been cultivated for thousands of years, offering both nutritional value and culinary versatility. Did you know? The phrase “like peas in a pod” originates from the perfect uniformity of peas within their pods.
18. Beets (Beetroots)
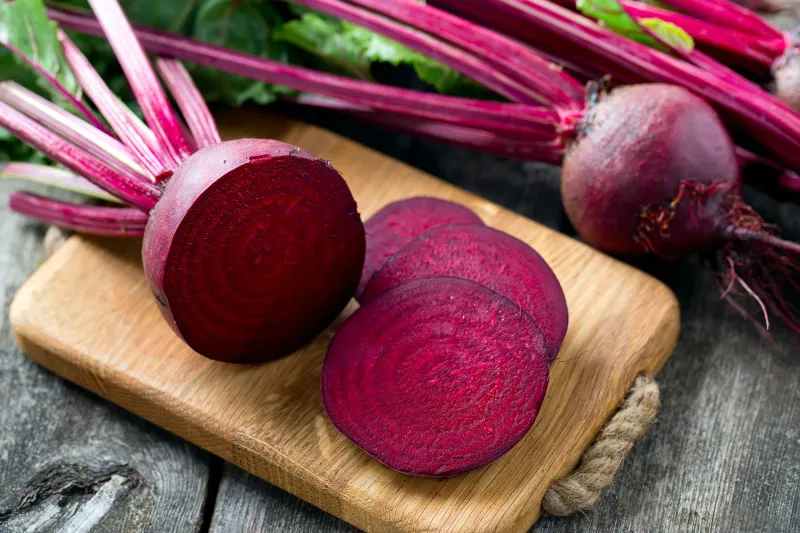

Beets, with their deep red color and earthy sweetness, are a versatile root vegetable. Valued for both their roots and greens, beets are cherished in various cuisines.
In Eastern European and Indian dishes, beets add a rich, vibrant hue and unique flavor. Their nutritional benefits are also noteworthy, providing essential vitamins and minerals.
Beyond their culinary uses, beets have historically been used for natural dyeing. Did you know? In Roman times, beets were used medicinally, believed to treat a variety of ailments. Today, they continue to add color and nutrition to meals.
19. Okra
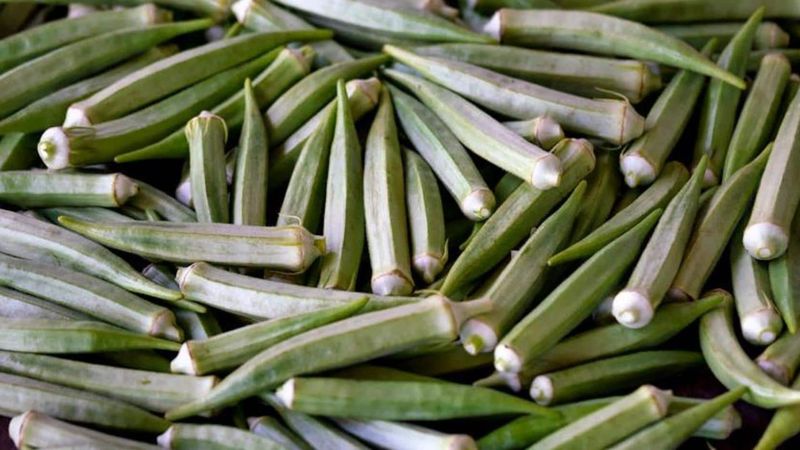

Okra, with its slender pods and unique texture, is a beloved vegetable in many regions. Essential in Southern U.S., West African, and Indian cuisines, okra is often stewed or fried.
Known for its ability to thicken dishes, okra is a staple in gumbo and other hearty meals. Its distinctive flavor and texture make it a favorite among adventurous eaters.
Historically, okra has been cultivated for centuries, with origins in Africa. Did you know? Okra seeds were once used as a coffee substitute during the American Civil War. Its culinary versatility and history make it a fascinating ingredient.
20. Pumpkin
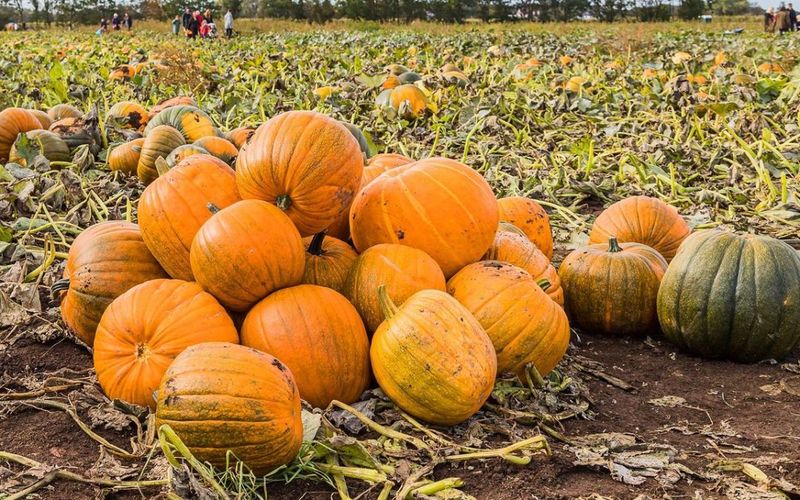

Pumpkins, with their bright orange hue and hearty flesh, are a versatile vegetable enjoyed on every continent except Antarctica. Often associated with autumn, pumpkins are used in pies, soups, and even savory stews.
Their mild, sweet flavor pairs well with a variety of spices, making them a favorite in both sweet and savory dishes. Native to North America, pumpkins have been cultivated for thousands of years.
Did you know? The largest pumpkin ever grown weighed over 2,600 pounds! Pumpkins’ adaptability and rich history make them a fascinating subject in the world of vegetables.
21. Celery
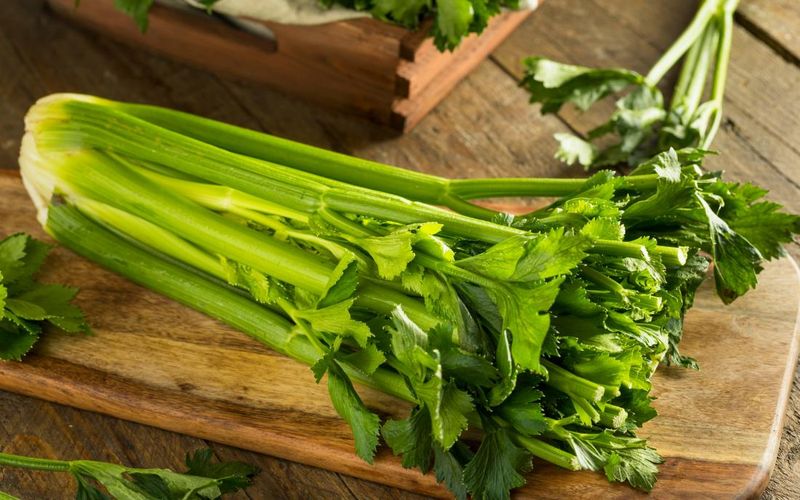

Celery, with its crisp stalks and aromatic base, is a staple in many kitchens. Often used as a base for soups, sauces, and salads, its subtle flavor enhances a variety of dishes.
In addition to its culinary uses, celery is also appreciated for its health benefits, known for its hydrating and low-calorie properties. Its crunchy texture makes it a popular snack, often paired with dips.
Celery has been cultivated since ancient times, with its origins in the Mediterranean region. Today, it continues to be a symbol of freshness and health in culinary traditions worldwide.
22. Radishes
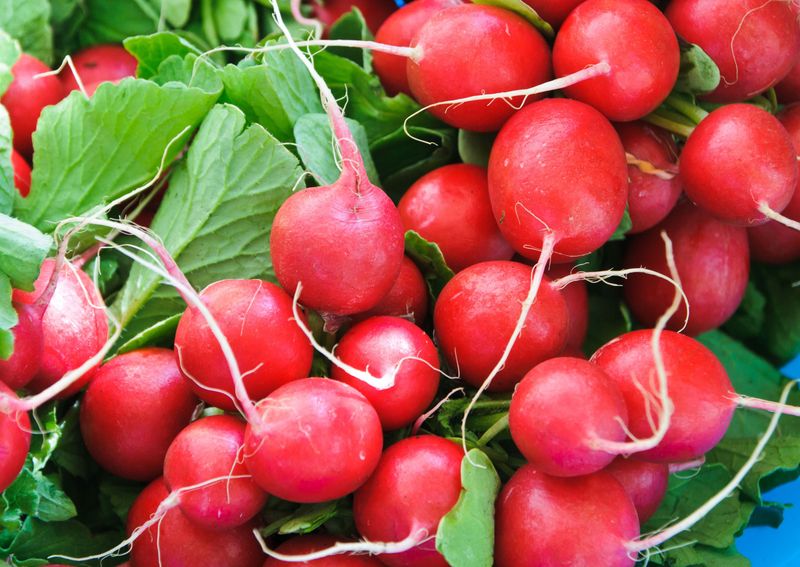

Radishes, with their peppery bite and vibrant red color, are a fast-growing root vegetable. Often eaten raw, they add a refreshing crunch to salads and sandwiches.
In Asian cuisines, radishes are commonly pickled, enhancing their flavor and preserving their crisp texture. Their quick growing time and adaptability make them a favorite for home gardeners.
Interestingly, radishes have been cultivated for thousands of years, with evidence of their use in ancient Egypt and Greece. Today, they continue to be appreciated for their unique flavor and versatility in dishes worldwide.
23. Turnips
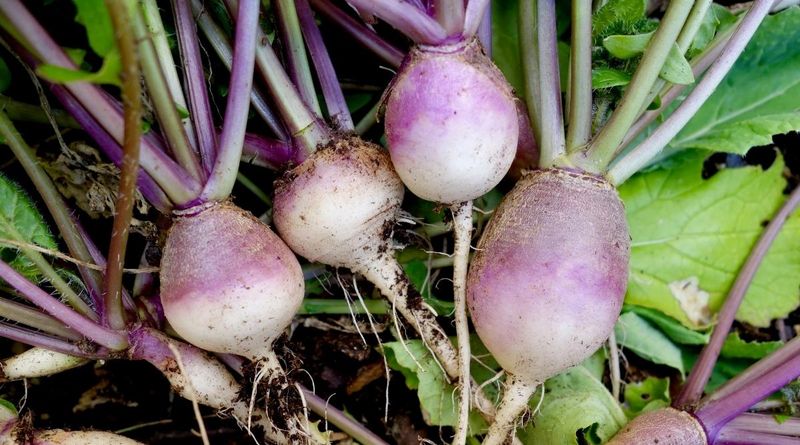

Turnips, with their creamy white roots and peppery flavor, are a cool-season vegetable with a rich history. Cultivated widely in Asia and Europe, turnips are valued for both their roots and greens.
In many cultures, they are a traditional ingredient in soups and stews, adding a hearty texture and flavor. Their adaptability to different climates and growing conditions makes them a reliable crop.
Did you know? Turnips have been used as a food source since ancient times, with evidence of their cultivation dating back to Roman times. Today, they continue to delight with their robust flavor.
24. Leeks
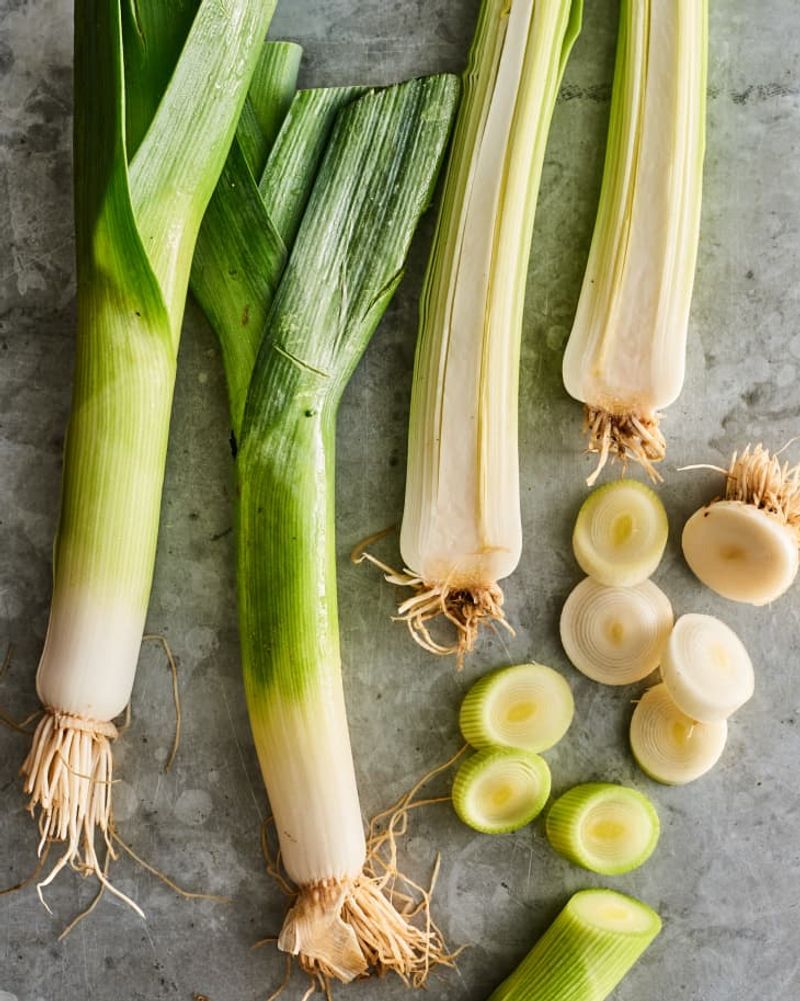

Leeks, with their mild onion-like flavor, are a cherished vegetable in many European and Mediterranean cuisines. Often used in soups and stews, their aromatic quality enhances a variety of dishes.
In France, leeks are a key ingredient in vichyssoise, a classic cold soup. Their subtle taste and tender texture make them a versatile addition to both simple and complex recipes.
Historically, leeks have been cultivated for centuries, with evidence of their use in ancient Egypt and Rome. Today, they continue to be appreciated for their unique flavor and versatility in the kitchen.
25. Chard (Swiss Chard)
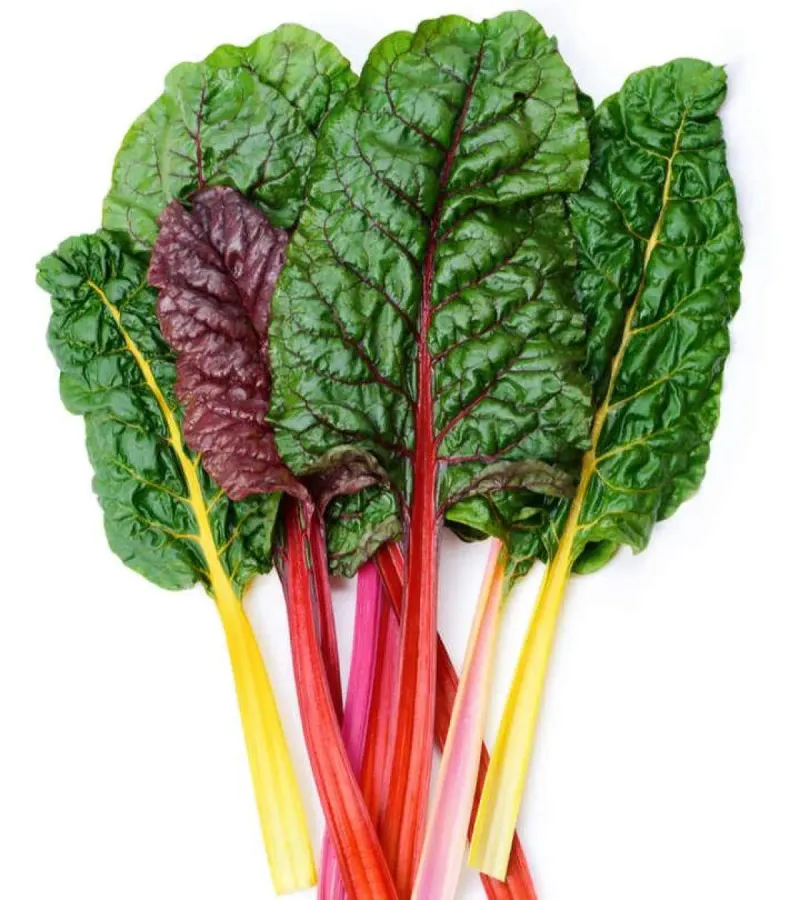

Chard, also known as Swiss chard, is a leafy green celebrated for its vibrant colors and nutritional benefits. Its tender leaves and crunchy stems make it a popular ingredient in Mediterranean diets.
Chard is often sautéed or added to soups and stews, providing a boost of vitamins and minerals. Its adaptability to different cooking methods makes it a versatile choice for many dishes.
Interestingly, chard is closely related to beets and shares a similar earthy flavor. Did you know? The ancient Greeks and Romans revered chard for its medicinal properties, believing it to promote health and vitality.
26. Shallots
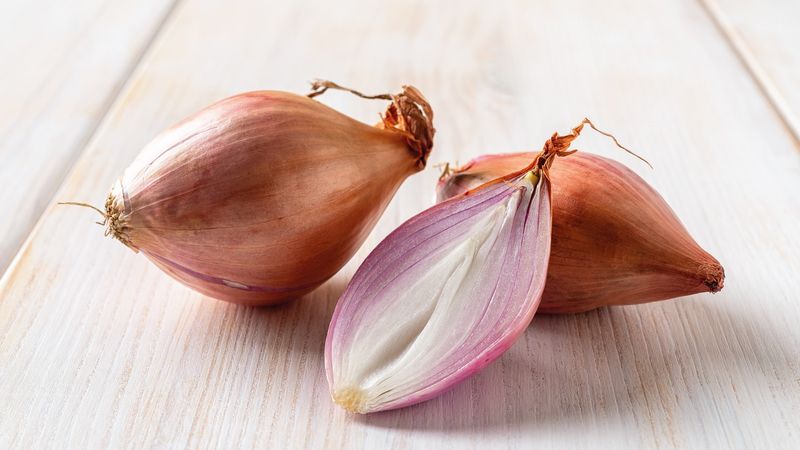

Shallots, with their delicate flavor and aroma, are a beloved ingredient in many kitchens. Closely related to onions and garlic, they offer a milder, more nuanced taste that enhances a variety of dishes.
Often used in sauces and dressings, shallots add depth and complexity without overpowering other flavors. Their versatility makes them a favorite for chefs and home cooks alike.
Did you know? Shallots have been cultivated for centuries, originally from Central and Southwest Asia. Today, they continue to be appreciated for their culinary flexibility and subtle flavor in cuisines worldwide.
27. Artichokes
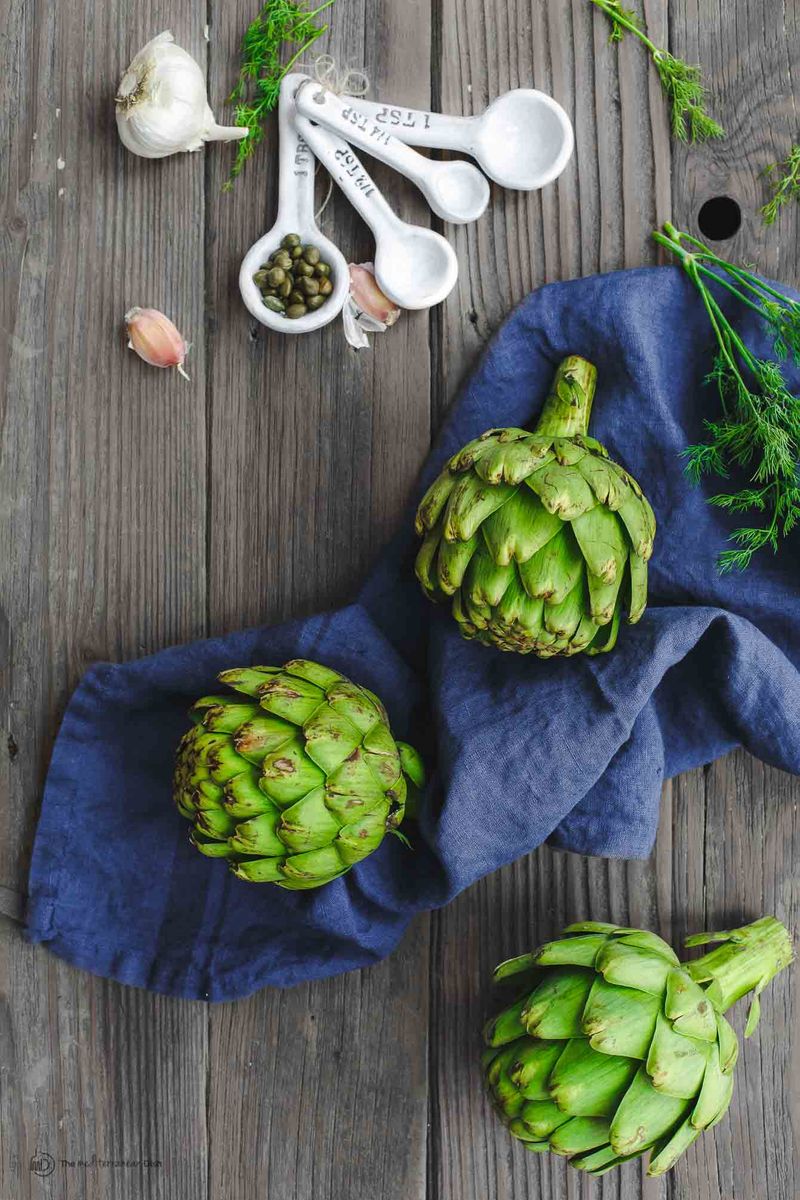

Artichokes, with their unique appearance and savory flavor, are a staple in Mediterranean cuisines. Known for their tender hearts and edible leaves, they are often steamed or grilled.
In Italy, artichokes are celebrated in dishes like carciofi alla romana, showcasing their versatility and rich taste. Their cultivation in Mediterranean climates is a testament to their adaptability and appeal.
Interestingly, artichokes have been cultivated since ancient times, with evidence of their use in Greek and Roman cuisine. Today, they continue to inspire culinary creativity and delight with their distinct flavor.
28. Yams (Dioscorea)
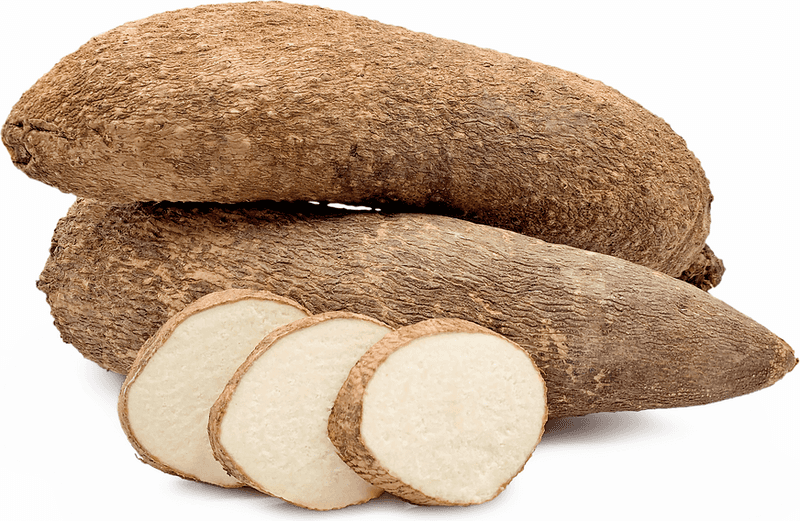

Yams, often confused with sweet potatoes, are a major root crop in Africa and Asia. Their starchy flesh and earthy flavor make them a versatile ingredient in savory and sweet dishes.
In many cultures, yams are a staple, providing essential nutrients and energy. Their ability to adapt to different climates and growing conditions makes them a reliable food source.
Did you know? In West Africa, yams are celebrated in festivals, symbolizing abundance and prosperity. Today, they continue to be a vital part of diets worldwide, cherished for their nutritional benefits and culinary versatility.
29. Cassava (Manioc)
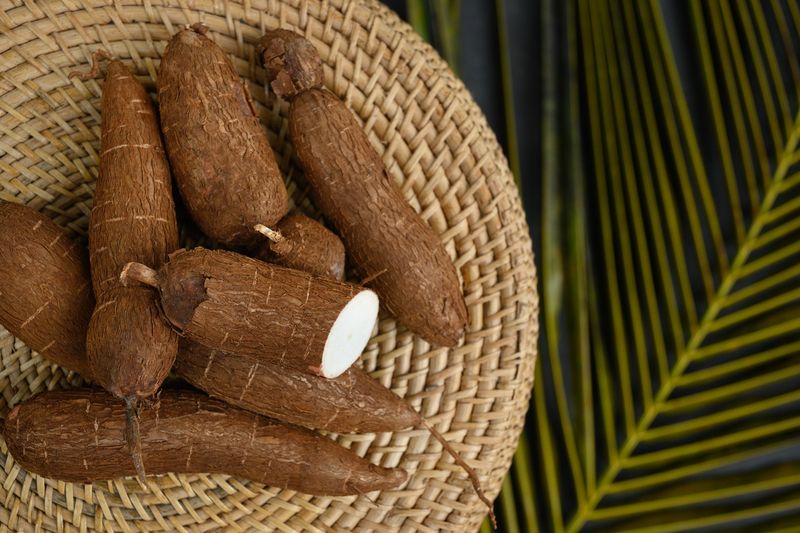

Cassava, also known as manioc, is a starchy root vegetable essential in tropical regions, particularly in Africa and South America. Its mild flavor and versatility make it a staple in many diets.
In many cultures, cassava is used to make dishes like tapioca and fufu, showcasing its adaptability. Beyond its culinary uses, cassava is also a significant source of carbohydrates and energy.
Did you know? Despite its importance as a food source, cassava must be cooked properly to eliminate toxic compounds. Its cultivation and use in diverse culinary traditions highlight its global significance.
30. Chinese Cabbage (Napa, Bok Choy)
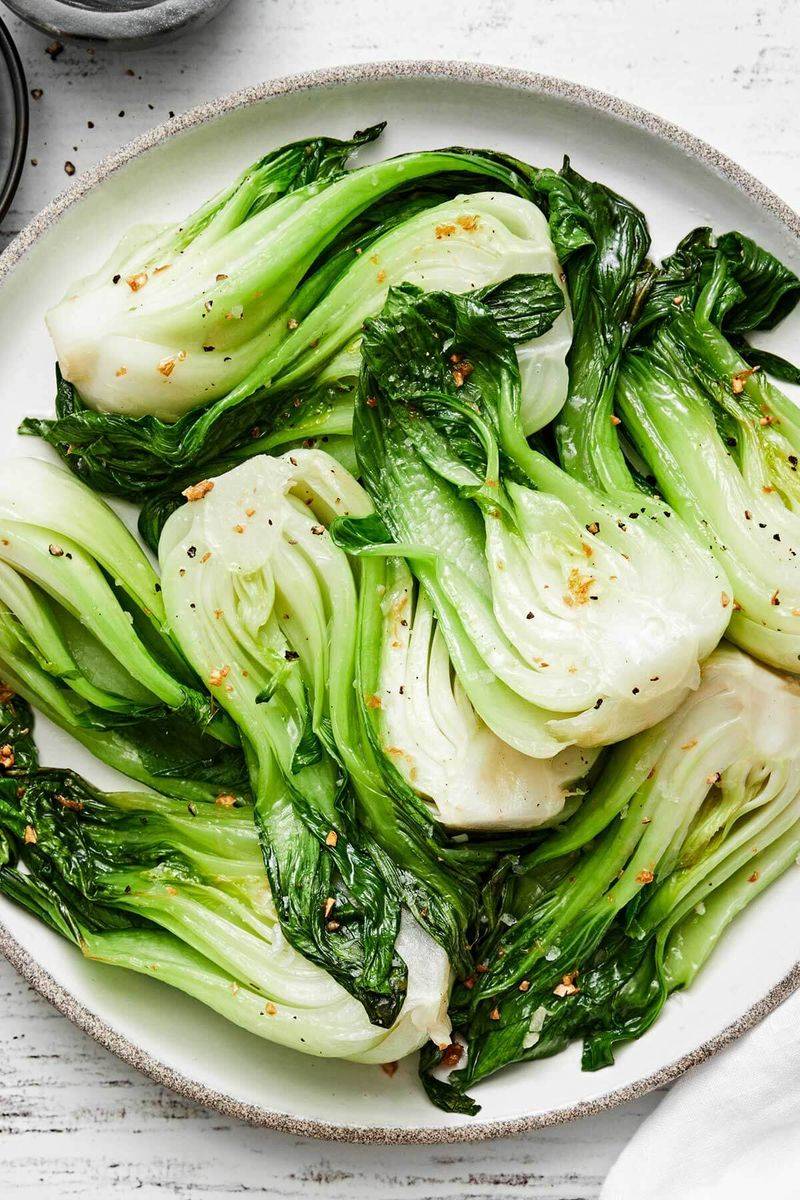

Chinese cabbage, with its tender leaves and mild flavor, is highly cultivated across East Asia. Known by varieties like napa and bok choy, it is a staple in many Asian cuisines.
Often used in stir-fries and soups, Chinese cabbage adds a refreshing crunch and subtle sweetness to dishes. Its versatility makes it a popular choice for both traditional and modern recipes.
Did you know? Chinese cabbage has been cultivated for over a thousand years, with a rich history in Chinese culinary traditions. Today, it continues to gain popularity worldwide for its nutritious qualities and delightful taste.
